Advanced education through VIROO
Learning by simulation has become mainstream in medical training. It is efficient, safe, more affordable than creating physical replicas. Virtual Reality when deployed in the area of practical simulation has tremendous advantages that are not just a vision into the future, they are a present day-to-day usable learning strategy for medical practices. Let’s dive deeper into how to succeed with this progressive integration.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Virtual Reality re-emerges strongly after COVID-19
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
At the beginning of 2020, virtual reality (VR) once again continued as a promising technology that even though highly advanced, had still not been exploited to its full potential in the healthcare sector. It is true that, over the last years, virtual reality has been gaining more and more awareness, gradually becoming more interesting as an advanced enterprise solution. Since it’s not new technology, we have become accustomed to reading different articles and news about the introduction of VR into early adopter sectors such as marketing, research and most common domestic use for entertainment purposes due to the arrival of affordable and high-quality hardware options on the market.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_separator color=”white”][vc_single_image image=”31994″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Then came the COVID-19 pandemic, and a new world where social distancing has been the key to containing its spread further. This has accelerated VR adoption exponentially, just like it has driven the digital migration and transformation work in all the areas.
Virtual reality and all-immersive technologies as a whole have exploded into the healthcare sector, bringing an innovative approach that is changing the techniques and methods of training and education, opening up new environments or scenarios that may be dangerous, limited, too expensive to recreate or even not possible in the real world.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Beyond this several studies have proven virtual reality to be more motivating and exciting when compared to traditional training. VR’s ability to unlock visceral sensations make it a tremendously powerful tool to train new skills and procedures with high retention.
The military sector is currently using virtual reality to train army personnel in bomb disposal, oil companies are recreating risk scenarios on oil platforms to keep their workers safe, and in the healthcare sector, medical students are accessing virtual operating rooms to learn and perform different surgical procedures that would not be possible to recreate in real life.
[/vc_column_text][vc_separator color=”white”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
A paradigm shift
Until now VR has been mostly associated with the gaming industry, but nowadays it is being used in almost all sectors of the economy. In particular, VR has always been positioned to be a magic bullet for the training and education sector.
A recent study by PwC researched (1) the effect of VR on learning and retaining social skills, for example. According to the report, the students participating using virtual reality assimilated information 4 times faster, are 3.75 times more emotionally connected to their educational material and are 4 times more concentrated in comparison with the students in a traditional classroom. In terms of skills application, those studying in virtual reality walked away with 275% more confidence than the rest of the people (not in VR) surveyed in the study.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
On a similar thread, Accenture conducted an industry-wide experiment to study the effectiveness of immersive learning through virtual reality. Participants were divided into two groups: one group watched an instructional video while the other participated in immersive VR training.
They then put the acquired knowledge into real practice and the overall accuracy and time to complete the task were measured. The experiment shows that the VR students showed 12% more accuracy and 17% faster course completion time than those who did it by traditional methods.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Virtual Reality in Medicine
When we talk about medicine, and we look at the most recent changes that have happened to medical practices like the complex needs of an ageing population, the increasing range of treatment options available, the interprofessional importance of care, and the complexity of health system services,… we come to a realization that everything is very different today than it was even just 10 years ago.
As a consequence, the way we train future physicians and update health professionals for clinical practice needs to be updated to meet new demands. It is no longer just a question of one person being able to remember or having easy access to the content, it is now a matter of how they use the infinite amount of information available, and how they analyse it and apply it to patient care.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
We have moved from memory-based learning to learning-by-doing, practices. Thanks to new technologies, over the last few years we have seen that training content has evolved in how it’s delivered, and we have seen how the introduction of certain game mechanics (gamification) has improved the content adherence of health professionals and students, providing a greater degree of motivation.
We are collectively undergoing a big jump in the quality of training methods, based on solving problems, improving training and communication skills (soft skills) by adding simulation techniques.
Simulation is an educational technique that involves the creation of situations that replicate real life, making health professionals able to act as they would do in real clinical practice while providing a safe environment in which a student can practice and even make mistakes without risk.
Simulations now play a crucial role with the introduction of VR, as a student using a VR headset can be fully immersed in an interactive virtual environment without distraction and with the feeling of “being there”. This application makes VR a highly efficient tool for teaching and training in medical simulation.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
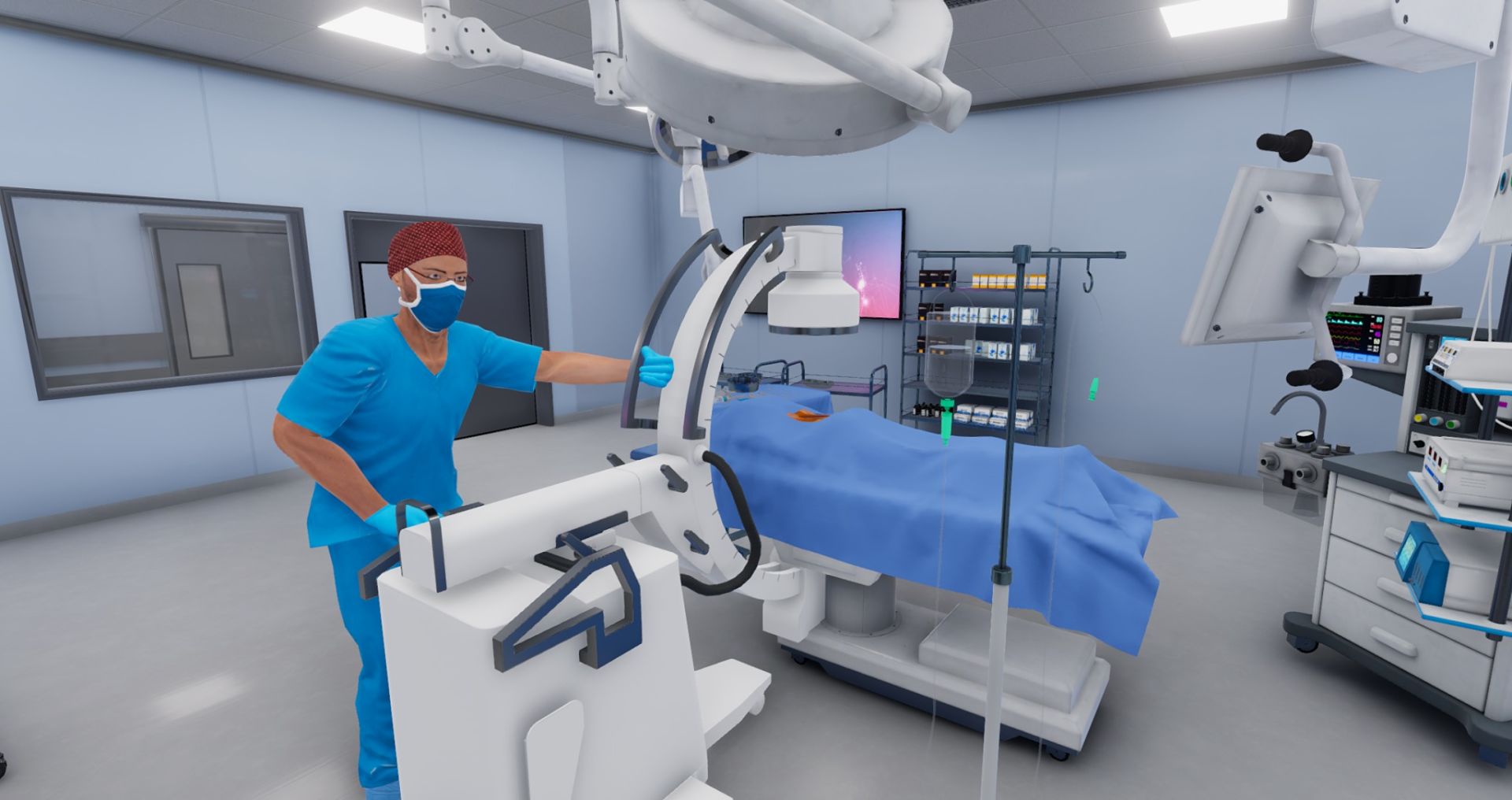
Multiuser VR Experiences
In VR, one can imagine several use cases in health: from an educational pill to show the mechanism of action when taking a medication, the advantages of release from an inhalation device, the application of a simple surgical technique, a virtual trip inside the human body, or a small game to educate young children about certain aspects of pathology. These are just some of the ideas that perfectly fit with the use of these technologies that have not been available till now in such an immersive medium.
However, do note that in all these cases mentioned there is a common denominator: these are all single-user experiences. Meaning only one user is immersed in the VR experience and just that person interacts with the content. So what happens in cases where educational or training processes need the participation of different team members to work together in a coordinated effort?
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”27938″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Essentially how can we simulate a multidisciplinary action in which a group of health professionals have to interact, communicate, and coordinate? An example of this would be training staff in the decision-making process at an emergency ward facing potential cases of COVID-19 infection. In this use case, let’s say it is necessary to involve different experts or even non-healthcare personnel: people who are in the admission area, (who probably first talk to potential patients), after admission, (triage phase), and if gravity requires it, to the isolation unit. In this type of case, it is very important to count on multi-user technology that allows collaboration and interaction in the simulated environment. Essentially they need to be trained by simulating a real situation, at a 1:1 scale that is as close to the real scenario as possible.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Virtual Reality On A Larger Scale
And it is precisely in this kind of situation in which VR technology reaches its highest level of innovation. If we need to have free mobility and simulate precisely real-world scale situations, the need for large scale virtual reality rooms is paramount.
Technologies such as Virtualware’s VIROO (3), allow for installations that can handle the reproduction of real-world situations, allowing for a large number of participants to interact with simulations that can easily be deployed according to their training needs.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”30848″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Immersive rooms such as VIROO are not only a technological solution for training, they are a powerful innovation tool that allows any organization, entity or institution to apply virtual reality into its own processes. VIROO allows for the easy deployment of real scale (1:1) Virtual Reality multi-user content, thanks to its innovative patented tracking system and software platform. It gives the power to manage, operate, and control immersive rooms of any size without the need for high technical skills, allowing teams to generate and deploy new content associated with their needs at the moment, and without having to develop a custom application. Recently, VIROO has also incorporated new functionalities that allow training sessions to be carried out from remote locations, so students and instructors can work simultaneously in the same virtual 3D environment as if they are in the same room.
This technology not only brings improved results in individual and team performance by simulating real situations, but it also reduces capital investment costs that go into physical replicas as well as associated operational training costs (travel and living expenses, etc.). VIROO has recently been awarded as “Enterprise VR Solution of the Year (2019)”, and was selected finalist as the best training solution for General Electric in the “VR Awards 2020”.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
sound investment in health education innovation
So what is the best way forward for the future of health education that we can start with now? Well, we have just seen that powerful technology is already at our disposal, so there is no reason to a standstill.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”2/3″][vc_column_text]
“Now is the moment to move forward, and take the next steps to go virtual. This new philosophy of training and education based on virtual simulation gives us the power to provide medical simulation centres the infrastructure for our health professionals to “learn by doing”, improving the quality interprofessional education at scale, regardless of geographic location”
Julio Alvarez, Health Business Manager, Virtualware
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”27506″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][gem_youtube video_id=”nDOO43GBp3c”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row” content_placement=”middle” parallax=”content-moving” css=”.vc_custom_1553695590409{margin-top: -25px !important;margin-bottom: 0px !important;padding-bottom: 35px !important;background-color: #179ad8 !important;}” el_class=”cont-cta”][vc_column width=”1/2″ el_class=”text-cta”][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1624349436479{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″ el_class=”btn-cta”][gem_button position=”center” style=”outline” size=”large” corner=”0″ border=”4″ icon_pack=”material” text=”BOOK A VIROO DEMO” text_color=”#ffffff” hover_text_color=”#179ad8″ border_color=”#ffffff” hover_border_color=”#ffffff” hover_background_color=”#ffffff” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fvirtualwareco.com%2Fcontact-us%2F%23contact-us|||”][/vc_column][/vc_row]